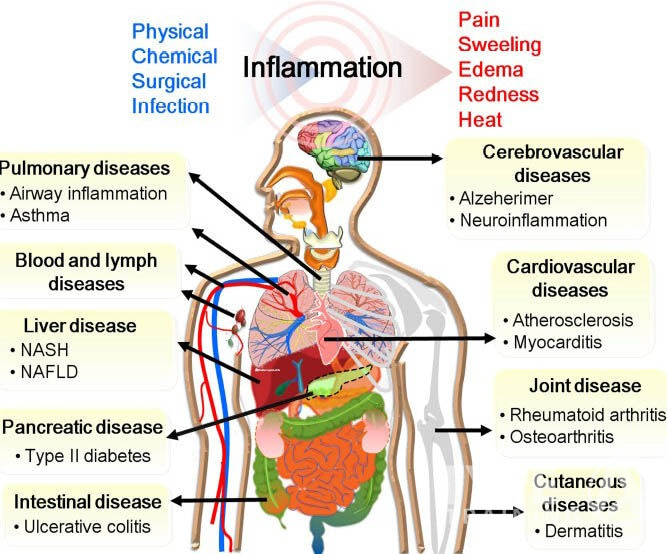
Inflammation is your body’s natural response to injury or infection. When functioning well, it helps you heal by sending white blood cells to the affected area. Yet, not all inflammation is helpful.
Understanding the inflammation health effects is crucial for recognizing how it impacts your body.
Chronic inflammation can lead to serious health issues if your body is constantly inflamed without a clear reason.
Many individuals overlook the inflammation health effects that can arise from prolonged exposure to stress and poor nutrition.
Popular posts:
Chronic inflammation plays a role in diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, leading to ongoing damage. This misguided response can cause pain and long-term health problems, impacting your overall well-being.
The inflammation health effects can manifest in various ways, often leading to chronic pain conditions.
Understanding the inflammation health effects is essential for recognizing how chronic inflammation impacts your overall health and well-being, as well as the inflammation health effects on various body systems.
Many studies focus on the inflammation health effects associated with lifestyle choices.
Understanding how lifestyle and diet influence inflammation can help you manage and potentially reduce chronic inflammation.
It’s important to understand the inflammation health effects of different food choices on your body.
Certain foods and habits can exacerbate this issue, so it’s important to learn how to make choices that support your health.
Key Takeaways
- Acute inflammation helps your body heal from injuries.
- Chronic inflammation can lead to severe health conditions.
- Diet and lifestyle choices play a significant role in managing inflammation.
Inflammation Health Effects on Overall Well-Being
Recognizing inflammation health effects on mental well-being can lead to better management strategies.
For more insights on the inflammation health effects, check out this informative video.
This video elaborates on the inflammation health effects and why it’s important to address them.
This section highlights the inflammation health effects and their significance in our daily lives, emphasizing the need for awareness and management.
Awareness of the inflammation health effects can help motivate lifestyle changes.
Inflammation is your body’s natural response to injury or infection. It’s crucial for healing but can cause problems when it becomes chronic.
Types of Inflammation
There are two main types: acute and chronic inflammation.
Acute inflammation happens quickly and lasts for a short time. It’s the body’s immediate response to sudden injuries, like cuts or infections.
Signs include redness, heat, swelling, and pain. This type helps start the healing process by sending white blood cells to the affected area.
On the other hand, chronic inflammation is long-lasting and can occur even without an obvious injury. This type can lead to health problems such as heart disease or arthritis.
It’s often caused by factors like poor diet, stress, or long-term exposure to irritants. Unlike acute inflammation, the signs are less noticeable but damaging over time.
Signs and Symptoms
Acute inflammation typically shows visible signs like redness and swelling. The affected area may feel warm and painful.
These symptoms result from the increased blood flow and immune activity trying to heal the injury.
Chronic inflammation symptoms are subtler. They can include ongoing fatigue, fever, and pain that persists without an apparent cause.
Additionally, it can lead to the gradual destruction of tissues, contributing to diseases like diabetes and cancer.
It’s important to recognize these signs early and seek medical advice to manage the underlying issues.
The Causes of Inflammation
Understanding how different triggers contribute to inflammation health effects is vital.
image credit: truebasics.com
Inflammation occurs due to various triggers. These can include infections, injuries, autoimmune disorders, and chronic diseases. Understanding the different causes can help you identify and manage inflammation effectively.
Identifying these inflammation health effects can empower you to make better health choices.
Infections and Injuries
When you get an infection or sustain an injury, your body’s immune system kicks into gear.
For example, if bacteria or a virus enters your body, white blood cells rush to the affected area. This response aims to fight off the invaders and promote healing.
This leads to symptoms like redness, warmth, pain, and swelling. Injuries, such as cuts or bruises, also trigger inflammation as your body works to repair damaged tissues.
Normal inflammation should be mild and help in healing. Excessive inflammation, however, can lead to complications and prolonged pain.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders cause your immune system to mistakenly attack your own tissues.
Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are examples of autoimmune conditions. In these cases, the body perceives its own cells as threats.
The immune system then launches an attack, leading to chronic inflammation.
You might experience ongoing pain, stiffness, and swelling in affected areas. Managing these disorders often requires medication to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases can also cause long-term inflammation.
Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and asthma are linked to chronic inflammation.
In chronic disease, low-level inflammation persists over time, contributing to the progression of the illness.
For example, in heart disease, inflammation can damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attacks.
Managing chronic inflammation often involves lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, along with medications to control symptoms.
Inflammation and Chronic Illness
Understanding the relationship between inflammation health effects and chronic illness can guide treatment options.
image credit: researchgate.net
Inflammation is a natural response that helps your body heal. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it may contribute to serious health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Chronic inflammation has notable inflammation health effects, impacting various bodily systems.
Heart Disease and Stroke
Chronic inflammation is linked to cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease and stroke.
When your body fights inflammation long-term, it can damage blood vessels and create plaque buildup. This buildup can narrow arteries and restrict blood flow, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
It’s crucial to address the inflammation health effects associated with heart disease and stroke.
Managing inflammation through lifestyle changes can significantly reduce these risks.
Diabetes and Obesity
Type 2 diabetes and obesity are closely connected to chronic inflammation.
Excess fat, particularly around the abdomen, causes inflammatory responses in your body. This inflammation affects insulin sensitivity, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
Addressing inflammation through diet, exercise, and weight management can improve insulin function and help control diabetes and obesity.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Arthritis
Inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis involve chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Symptoms include abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Similarly, rheumatoid arthritis is a condition where inflammation affects the joints, causing pain and swelling.
Treatments aim to reduce inflammation to manage symptoms effectively.
Cancer
Be aware of how inflammation health effects can influence diabetes and obesity management.
Chronic inflammation can also contribute to cancer development.
Long-term inflammation may cause DNA damage and support the growth of cancer cells.
Researchers are continually studying inflammation health effects related to cancer development.
Conditions like hepatitis can lead to liver cancer, while inflammatory responses in the body may increase the risk of other types of cancer.
Reducing inflammation is crucial in lowering cancer risk.
For more detailed information on how inflammation links to these conditions, visit relevant resources like Mayo Clinic and Harvard Health.
Lifestyle Factors and Inflammation
Understanding the inflammation health effects of lifestyle factors can lead to healthier habits.
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact inflammation in your body. What you eat, how active you are, your stress levels, and your sleep can either increase or reduce inflammation.
Diet and Nutrition
Your diet plays a crucial role in inflammation.
Diet choices greatly influence the inflammation health effects on your body.
Eating foods high in trans fats, like fried foods and baked goods, can increase inflammation. Processed foods containing added sugars also contribute.
Meanwhile, anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains, can help reduce inflammation.
Certain fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Olive oil and nuts are other good options.
A balanced diet rich in these foods can help manage and lower inflammation levels in your body.
Implementing an anti-inflammatory diet can significantly reduce inflammation health effects.
Exercise and Body Weight
Regular exercise can reduce inflammation.
Activities like walking, running, and swimming help keep your weight in check and decrease inflammatory markers. Exercise improves your body’s metabolism and enhances overall immune function.
Obesity is linked to higher inflammation.
Losing weight through exercise and a proper diet can lower these risks.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity weekly. Maintaining a healthy weight is key to controlling inflammation.
Stress and Sleep
Chronic stress impacts inflammation health effects, emphasizing the need for stress management.
Chronic stress can increase inflammation.
Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress.
Reducing stress through these techniques can have a positive effect on your body’s inflammatory response.
Sleep is another critical factor.
Poor sleep habits, like getting less than 6 hours a night, can increase inflammation.
Prioritizing good sleep hygiene can mitigate inflammation health effects.
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and ensuring 7-8 hours of sleep each night can help reduce inflammatory markers. Good sleep hygiene is essential for overall health and wellness.
Diagnosing Inflammation
Early detection and accurate diagnosis of inflammation are important for appropriate treatment.
There are several ways to diagnose inflammation, including specific medical tests and a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider.
Medical Tests
To diagnose inflammation, doctors often rely on blood tests.
The most common are the C-reactive protein (CRP) test and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test.
CRP levels rise when there is inflammation in the body. ESR measures how quickly red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube, which increases in the presence of inflammation.
White blood cell counts may also be elevated, as white blood cells are key players in the body’s immune response.
In some cases, more specialized tests like cytokine panels can provide additional details.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, can show inflammation in tissues and organs.
These are particularly useful for conditions like arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease. Accurate diagnosis via these tests helps doctors create a tailored treatment plan.
Physical Examination
During a physical exam, your doctor will look for signs of inflammation such as redness, swelling, and warmth around joints or tissues.
You might be asked about pain levels, stiffness, and any recent injuries or infections.
Checking the range of motion in affected areas can help determine the extent of inflammation.
Your healthcare provider may also examine your lymph nodes for any signs of swelling. Sometimes, they will palpate the abdomen if digestive inflammation is suspected.
Combining the results of physical examinations with medical tests helps doctors get a clearer picture of what might be causing the symptoms. This helps in identifying the right course of treatment.
For more detailed explanations, you can visit Harvard Health’s article on inflammation and the Cleveland Clinic’s guide on inflammation.
Treatments for Inflammation
image credit: naturalhealinghawaii.com
There are different ways to handle inflammation, including medications, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes. Each method helps reduce inflammation and ease symptoms.
Medications
Medications can help manage inflammation health effects effectively.
A common treatment for inflammation is NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs).
Consulting a healthcare professional can help address inflammation health effects appropriately.
Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen help lower inflammation, reduce pain, and bring down fevers.
Another medication that can help is aspirin, which can also reduce swelling.
For more severe cases, doctors may prescribe corticosteroids. These drugs can be very effective but might have more serious side effects if used long-term.
Taking these medications as directed is key to avoiding possible side effects. Always consult with your doctor before starting any new medication.
Natural Remedies
Some people find relief through natural methods, like using turmeric.
Turmeric contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil and flaxseeds, also help to reduce inflammation.
Natural remedies may also play a role in reducing inflammation health effects.
Foods rich in these fats can be added to your diet or taken as supplements.
Vitamin D plays a role in immune system health and may help reduce inflammation.
Spending time in the sun and eating vitamin D-rich foods like salmon, or taking supplements, can keep your levels up.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Your lifestyle can impact inflammation.
Eating an anti-inflammatory diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help reduce chronic inflammation.
Foods like berries, leafy greens, nuts, and olive oil are good choices.
Regular exercise is also important. Engaging in physical activities like walking, swimming, or yoga helps manage weight and lowers inflammation.
Getting enough sleep and reducing stress are also crucial.
Stress can worsen inflammation, so finding ways to relax, like meditation or hobbies, can be beneficial.
Dietary Influence on Inflammation
Assessing dietary influence on inflammation health effects is essential for long-term health.
Certain foods can either reduce or increase inflammation in your body. Knowing what to eat and what to avoid is crucial for managing chronic inflammation.
Reduce Your Sugar Intake
Consuming too much sugar can lead to inflammation.
Reducing sugar can help lessen inflammation health effects.
The average American eats around 68 grams of added sugar daily, far exceeding the recommended limits.
This excessive sugar intake can contribute to chronic inflammation and related health issues like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Aim to keep your added sugar intake to less than 6% of your total daily calories.
For instance, men should limit their sugar consumption to 36 grams (9 teaspoons) and women to 24 grams (6 teaspoons) per day.
You can do this by reducing sugary drinks, desserts, and packaged foods that often contain hidden sugars. Checking food labels for sugar content can help you make healthier choices.
Pro-Inflammatory Foods
Certain foods can increase inflammation.
Be mindful of how certain foods contribute to inflammation health effects.
Processed and fried foods often contain trans fats, which are known to trigger inflammation.
Refined carbohydrates such as white bread, pasta, and sugary snacks can also cause spikes in blood sugar, leading to inflammation.
Red meat and processed meats, like bacon and sausage, contain saturated fats that can promote inflammatory markers in the body.
Additionally, foods high in omega-6 fatty acids, like soybean and corn oil, should be limited as they can contribute to inflammation when consumed in excess.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Eating foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties can help combat chronic inflammation.
Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables, particularly green leafy vegetables, which are high in antioxidants that fight inflammation.
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can counteract negative inflammation health effects.
Whole grains, such as brown rice and oats, provide fiber which supports gut health and reduces inflammation.
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, like salmon and mackerel, as well as plant-based sources like flax seeds and walnuts, are effective in lowering inflammation.
Nuts, olive oil, and other unsaturated fats also help reduce inflammatory markers.
How Tea and Spices Can Benefit You
Tea and certain spices have powerful anti-inflammatory benefits.
Green tea, in particular, is rich in polyphenols and antioxidants that help reduce inflammation. Black and white teas also offer similar benefits.
Incorporating spices like turmeric, ginger, garlic, and cinnamon into your meals can further aid in reducing inflammation.
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound known for its strong anti-inflammatory effects. Ginger and garlic add flavor and health benefits, making them easy additions to your diet.
Using these teas and spices regularly can be a simple and effective way to boost your anti-inflammatory efforts.
Utilizing tea and spices can support efforts to manage inflammation health effects.
Mental Health and Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to various mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. Research shows inflammation affects brain chemistry and can influence emotional well-being.
Depression and Anxiety
Chronic inflammation can impact your mental health by altering your brain’s chemistry and structure. This link is particularly significant in conditions like depression and anxiety.
For example, inflammation may interfere with neurotransmitters, which are crucial for mood regulation.
You may experience symptoms such as fatigue and sleep disturbances. These physical symptoms can further exacerbate feelings of depression and anxiety.
Studies reveal that people with higher levels of inflammation often exhibit more severe depressive and anxiety symptoms.
Understanding the connection between chronic inflammation and mood disorders can inform treatment of inflammation health effects.
Higher inflammation markers, like C-reactive protein (CRP) or cytokines, are commonly observed in individuals suffering from these mental health issues. Chronic stress also contributes to inflammation, worsening these conditions.
Inflammation-Induced Mood Disorders
Mood disorders, including bipolar disorder, may also be tied to chronic inflammation.
Inflammation can disrupt brain processes, leading to mood swings and instability.
Researchers have found that individuals with mood disorders often have elevated markers of inflammation.
Inflammatory cytokines can affect how you process emotions and stress, potentially leading to mood disorders. This disruption may impair emotional attention and reaction to stressors, influencing your overall mood and emotional health.
Chronic inflammation might also contribute to other mood-related symptoms, such as irritability and anger.
Preventing Inflammation
Exercise regularly. Physical activity helps reduce inflammation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, like brisk walking or cycling, most days of the week.
Choose plenty of anti-inflammatory foods.
These include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. For example, blueberries, leafy greens, and nuts can help lower inflammation.
Manage stress effectively. Chronic stress can increase inflammation.
Effective stress management can alleviate inflammation health effects.
Try techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to keep stress in check.
Prioritize good sleep hygiene. Getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night helps control inflammation.
Keep a regular sleep schedule and create a restful sleep environment.
Focus on weight management. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce inflammation. Excess fat, especially around the abdomen, can release inflammatory substances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Inflammation can be a body’s natural response to injury or infection, but it can also lead to significant health problems if it becomes chronic. Here you will find answers to common questions about identifying, managing, and understanding the impacts of inflammation.
How can you identify the presence of inflammation in your body?
You can identify inflammation by looking for signs such as redness, swelling, pain, and warmth around a wound or infection site. These symptoms are usually clear indicators of acute inflammation.
What are the primary causes of inflammation?
Common causes of inflammation include infections, injuries, and exposure to harmful substances.
Chronic inflammation may stem from conditions like autoimmune disorders, prolonged stress, and lifestyle factors like poor diet and lack of exercise.
What strategies can effectively reduce inflammation?
To reduce inflammation, consider lifestyle changes like adopting a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can also help manage symptoms.
What are common diseases associated with inflammation?
Diseases linked to inflammation include rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and psoriasis.
Conditions such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes are also connected to chronic inflammation.
What are the potential long-term effects of chronic inflammation?
Long-term chronic inflammation can lead to severe health problems like cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Being aware of potential long-term inflammation health effects can motivate preventive measures.
It can also deteriorate overall health by affecting tissues and organs over time.
What are the classic signs that indicate inflammation?
Classic signs of inflammation include redness, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function in the affected area. These symptoms occur as your body’s immune response works to protect and heal the affected tissues.