If you are a senior living with diabetes, exercise is an important part of managing your condition. Exercise can help you control your blood sugar levels, improve your cardiovascular health, and maintain your overall well-being. However, it is essential to approach exercise with caution and take necessary precautions to avoid any complications.
As you age, your body may become more susceptible to health issues, and diabetes can further increase these risks. It is crucial to understand how diabetes affects your body and how exercise can help manage your condition. By incorporating exercise into your daily routine, you can improve your insulin sensitivity, lower your
To make exercise a safe and effective part of your diabetes management plan, it is essential to create a personalized exercise routine that considers your health concerns, fitness level, and lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the benefits of exercise for seniors with diabetes, types of exercises that are safe and effective, and tips for creating an exercise routine that works for you. We will also discuss nutrition and other lifestyle considerations that can help you manage your diabetes.
Key Takeaways
- Exercise is an essential component of managing diabetes for seniors, but it is crucial to approach it with caution and take necessary precautions.
- Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, lower
blood pressure , and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. - Creating a personalized exercise routine that considers your health concerns, fitness level, and lifestyle is crucial for making exercise a safe and effective part of your diabetes management plan.
Understanding Diabetes in Seniors
Popular posts:
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects many older adults. It occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, but it can also develop in older adults. In type 1 diabetes, your body does not produce insulin, which is a hormone that helps your body use blood sugar for energy.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes in older adults. In type 2 diabetes, your body does not use insulin properly, which is called insulin resistance. Over time, your body may not make enough insulin, and your blood sugar levels can become too high.
Symptoms of diabetes in seniors may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, blurry vision, fatigue, and slow healing of wounds. It’s important to get tested for diabetes, especially if you have any of these symptoms.
The A1C test is a blood test that measures your average blood glucose levels over the past three months. The A1C test is an important tool for managing diabetes, as it can help you and your healthcare provider determine how well you are managing your blood glucose levels.
Hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose levels, can be dangerous for seniors with diabetes. It can lead to complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney damage. It’s important to monitor your blood glucose levels regularly and work with your healthcare provider to keep your levels within a healthy range.
According to the National Institute on Aging, “physical activity is one of the most important things you can do to help manage your diabetes.” Exercise can help your body use insulin more effectively, which can help lower your blood glucose levels. It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
“Physical activity is essential for maintaining good health and managing diabetes.” – National Institute on Aging
Overall, understanding diabetes and its symptoms is important for seniors. Regular blood tests and monitoring of blood glucose levels can help seniors manage their diabetes and prevent complications. Exercise can also be an effective tool for managing diabetes, but it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
Exercise and Diabetes Management
Regular exercise is an essential part of managing diabetes, especially for seniors. Physical activity helps to control blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve overall well-being. You should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, as well as strength training exercises that work all major muscle groups at least two days per week.
Aerobic activity is any activity that increases your heart rate and breathing, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Resistance training, such as weight lifting or using resistance bands, helps to build muscle strength and improve balance. Both types of exercise are important for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
When exercising, it’s essential to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. Exercise can cause a drop in blood sugar, so it’s important to check your levels before, during, and after exercise. If your blood sugar is too low, eat a small snack before exercising, such as a piece of fruit or a granola bar.
“Exercise improves blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes, reduces cardiovascular risk factors, contributes to weight loss, and improves well-being,” says a source. Regular exercise may also prevent or delay type 2 diabetes development.
In addition to aerobic and resistance training, seniors may also benefit from activities that focus on balance, flexibility, and relaxation, such as yoga or Pilates. These activities can help to improve muscle tone, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being.
Overall, exercise is an essential part of managing diabetes for seniors. By incorporating regular physical activity into your routine, you can help to control blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve overall health and well-being.
Health Concerns and Precautions
As a senior with diabetes, it is important to take certain health concerns and precautions before and after exercising. Always consult with your doctor or healthcare professional before starting any new exercise routine. They can help you create a safe and effective plan that works for you.
One of the main concerns for seniors with diabetes is hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar. This can occur during or after exercise, especially if you take certain medications. To prevent hypoglycemia, make sure to check your blood sugar before, during, and after exercise. If your blood sugar is low, have a snack or glucose tablets on hand to raise it quickly. Hard candy can also work in a pinch.
Nerve damage is another concern for seniors with diabetes. This can lead to a loss of sensation in your feet, making it difficult to feel injuries or blisters. To prevent nerve damage, make sure to wear proper footwear that fits well and doesn’t rub or cause blisters. Check your feet regularly for any signs of injury and report any problems to your doctor or healthcare provider immediately.
Finally, seniors with diabetes are at a higher risk for amputation due to poor circulation and nerve damage. To prevent this, make sure to check your feet regularly, wear proper footwear, and avoid any activities that could cause injury or damage to your feet.
Remember, exercise is an important part of managing your diabetes, but it’s important to take the necessary precautions to keep yourself safe and healthy. As Harvard Health states, “Exercise is one of the best things you can do for your health. But if you have diabetes, it’s important to take some precautions to make sure you exercise safely.”
Benefits of Exercise for Diabetic Seniors
Exercise is an essential component of diabetes management, especially for seniors. Engaging in regular physical activity can provide numerous benefits for diabetic seniors, including:
- Weight management: Exercise can help you maintain a healthy weight or lose weight if you are overweight or obese. Losing even a small amount of weight can improve your blood sugar control and reduce your risk of heart disease and other complications.
- Heart health: Exercise can help lower your
blood pressure , cholesterol, and triglyceride levels, all of which are risk factors for heart disease. Regular exercise can also improve your heart health and reduce your risk of stroke. - Blood sugar control: Exercise can help lower your blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. This means that your body can use insulin more effectively to control your blood sugar levels.
- Cancer prevention: Exercise has been shown to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including breast and colon cancer.
- Kidney disease prevention: Exercise can help prevent or delay the onset of kidney disease, which is a common complication of diabetes.
- Improved well-being: Exercise can boost your mood, reduce stress, and improve your overall quality of life.
According to Dr. Ronald Sigal, a professor of medicine at the University of Calgary, “Exercise is the most potent medicine that you can take for diabetes.”
While there are many benefits to exercising as a diabetic senior, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and limitations. For example, seniors may be more prone to falls and injuries, so it is important to choose exercises that are safe and appropriate for your fitness level and health status.
Here is a pros and cons table to help you weigh the benefits and risks of different types of exercise:
| Type of Exercise | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Training | Can be tailored to your individual needs and fitness level | Can be expensive |
| Yoga | Can improve flexibility, balance, and relaxation | May not provide enough cardiovascular exercise |
| Pilates | Can improve core strength and posture | May not provide enough cardiovascular exercise |
Overall, the benefits of exercise for diabetic seniors far outweigh the risks. By incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine, you can improve your blood sugar control, reduce your risk of complications, and improve your overall health and well-being.
Types of Exercises for Seniors with Diabetes
Regular exercise is an essential part of diabetes management for seniors. It can improve blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and help maintain a healthy weight. Here are some types of exercises that are suitable for seniors with diabetes:
Endurance Exercises
Endurance exercises, also known as aerobic exercises, are activities that increase your heart rate and breathing. They can help improve your cardiovascular health and lower blood sugar levels. Some examples of endurance exercises include:
- Brisk walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Dancing
Flexibility Exercises
Flexibility exercises can help improve your range of motion and prevent injuries. They are also a great way to relax and reduce stress. Some examples of flexibility exercises include:
- Stretching
- Yoga
- Tai chi
Balance Exercises
Balance exercises can help improve your stability and prevent falls. They are especially important for seniors with diabetes, who may have nerve damage or other complications that affect their balance. Some examples of balance exercises include:
- Standing on one foot
- Heel-to-toe walking
- Tai chi
Housework
Housework can be a great way to stay active and burn calories. Activities like cleaning, gardening, and doing laundry can help you stay active throughout the day.
It is important to choose exercises that you enjoy and are comfortable doing. Start with low-impact exercises and gradually increase the intensity and duration as your fitness level improves. Remember to check your blood sugar before and after exercise and stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. If you experience any pain or discomfort during exercise, stop immediately and consult your doctor.
Creating an Exercise Routine
As an older adult with diabetes, exercising regularly is crucial to your overall health. Creating a consistent exercise routine can help you form a healthy habit and manage your diabetes symptoms. Here are some tips to help you create an exercise routine that works for you:
1. Set realistic goals: Start with small goals that you can achieve and gradually increase them as you progress. For example, start with a 10-minute walk every day and gradually increase to 30 minutes a day.
2. Find an exercise you enjoy: Choose an exercise that you enjoy doing, whether it’s walking, swimming, or dancing. This will make it easier for you to stick to your routine.
3. Involve your family and community: Exercise with your family or join a community exercise group. This can help you stay motivated and make exercising more enjoyable.
4. Work with a personal trainer: If you’re new to exercising or have any health concerns, consider working with a personal trainer. They can help you create a safe and effective exercise routine.
5. Try yoga or pilates: Yoga and Pilates are low-impact exercises that can help improve your flexibility, balance, and strength. They are also great for reducing stress and anxiety.
According to Dr. Ronald Sigler, MD, an endocrinologist at Providence Saint John’s Health Center, “Yoga is a great way to exercise if you have diabetes. It can help lower blood sugar levels, reduce stress, and improve overall health.”
By creating a consistent exercise routine that works for you, you can improve your overall health and manage your diabetes symptoms. Remember to always consult with your doctor before starting any new exercise routine.
Here’s A Sample Workout Routine For An Older Adult With Diabetes:
- Brisk walking: 30 minutes, 5 times per week.
- Start with a warm-up of 5-10 minutes of slow walking.
- Increase your pace to a brisk walk for 20-30 minutes.
- Cool down with 5-10 minutes of slow walking.
- Resistance band curls: 2 sets of 10-12 reps, with 30 seconds of rest between sets.
- Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the ground.
- Hold a resistance band with both hands, palms facing up.
- Curl the band towards your chest, squeezing your biceps, then release and repeat.
- Bodyweight squats: 2 sets of 10-12 reps, with 30 seconds of rest between sets.
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Bend your knees and lower your hips until your thighs are parallel to the ground, creating a 90-degree angle.
- Push back up to the starting position and repeat.
- Seated leg extensions: 2 sets of 10-12 reps, with 30 seconds of rest between sets.
- Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the ground.
- Extend one leg out in front of you, keeping your foot flexed.
- Lower your leg back down to the starting position and repeat on the other leg.
Older adults with diabetes should start with lighter weights and lower intensity exercises before gradually increasing the weight and intensity. It is also important to maintain proper form, engage the correct muscles, and avoid jerky or sudden movements. Seniors should also listen to their bodies and stop exercising if they experience pain or discomfort.
This sample workout routine provides a starting point for older adults with diabetes who want to try exercise. However, older adults with diabetes should consult with their doctor before starting any new exercise program to ensure that it is safe for them. They should also monitor their blood sugar levels before and after exercise, and make any necessary adjustments to their medication or food intake.
Nutrition and Diabetes
Maintaining a healthy diet is an essential part of managing diabetes for seniors. By making healthy food choices, you can help control your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Healthy Eating
A healthy eating plan for seniors with diabetes should include a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It’s important to limit foods that are high in saturated and trans fats, added sugars, and sodium.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, so it’s essential to choose the right kind and amount of carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are better for managing diabetes than simple carbohydrates, such as candy, soda, and other sugary foods.
Hunger
Managing hunger is also important when it comes to diabetes and nutrition. Eating small, frequent meals throughout the day can help keep blood sugar levels stable and prevent overeating. It’s also important to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and other low-calorie beverages.
“A healthy diet is a cornerstone of diabetes management. By making healthy food choices, you can help control your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.” – NIDDK
Good and Bad Foods
Here is a table of some good and bad food choices for seniors with diabetes:
| Good Foods | Bad Foods |
|---|---|
| Fruits and vegetables | Candy and sugary desserts |
| Whole grains | White bread and refined grains |
| Lean proteins (chicken, fish, beans) | Processed meats (hot dogs, bacon) |
| Healthy fats (avocado, nuts, olive oil) | High-fat dairy (cheese, butter) |
By making smart food choices, you can help manage your diabetes and reduce the risk of complications.
Other Lifestyle Considerations
In addition to regular exercise, there are other lifestyle factors that can impact your diabetes management. By paying attention to these factors, you can better control your blood sugar levels and improve your overall health.
Sleep
Getting enough sleep is important for everyone, but it is especially important if you have diabetes. Lack of sleep can cause your blood sugar levels to rise, making it harder to manage your diabetes. Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep each night to help keep your blood sugar levels stable.
Smoking
Smoking is harmful to your health in many ways, and it can be particularly dangerous if you have diabetes. Smoking can increase your risk of developing complications from diabetes, such as heart disease and nerve damage. If you smoke, it’s important to quit as soon as possible.
“Smoking is the leading preventable cause of death worldwide. It increases the risk of developing diabetes and can make it harder to control blood sugar levels in people who already have the disease.” – American Diabetes Association
Anxiety
Anxiety and stress can cause your blood sugar levels to rise, making it harder to manage your diabetes. It’s important to find ways to manage your stress, such as through meditation, deep breathing exercises, or talking to a therapist.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia
There is some evidence to suggest that there may be a link between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. While more research is needed to fully understand this connection, it’s important to take steps to protect your brain health. This includes staying physically active, eating a healthy diet, and staying mentally engaged.
Arthritis
Arthritis can make it harder to exercise, but it’s still important to stay active if you have diabetes. Talk to your doctor about exercises that are safe for you to do, such as swimming or yoga. You may also want to consider working with a physical therapist to develop a safe and effective exercise program.
By paying attention to these lifestyle factors, you can improve your diabetes management and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Challenges and Solutions
As you age, managing diabetes becomes more challenging. You may experience joint pain, stiffness, and a higher risk of falling. Additionally, coexisting geriatric syndromes and logistical issues unique to long-term care facilities can further complicate management. Here are some challenges you may face and solutions to overcome them.
Joint Pain and Stiffness
Joint pain and stiffness can make it difficult to exercise, but it’s crucial to stay active to manage diabetes. Low-impact exercises like yoga and Pilates can help reduce joint pain while improving flexibility and balance. A certified personal trainer can also help you design an exercise plan that is safe and effective for your individual needs.
Risk of Falling
Falling is a significant concern for seniors, but regular exercise can help improve balance and reduce the risk of falls. Focus on exercises that improve balance, such as standing on one foot or walking heel-to-toe. A personal trainer can also help you develop an exercise plan that includes balance and strength training.
Abdomen and Back Pain
Abdominal and back pain can make it difficult to exercise, but it’s crucial to stay active to manage diabetes. Low-impact exercises like walking or swimming can help reduce pain while improving cardiovascular health. A personal trainer can also help you develop an exercise plan that strengthens your core muscles, which can help reduce pain and improve posture.
Foot and Leg Pain
Foot and leg pain can make it difficult to exercise, but it’s crucial to stay active to manage diabetes. Low-impact exercises like cycling or water aerobics can help reduce pain while improving cardiovascular health. A personal trainer can also help you develop an exercise plan that improves circulation and reduces pain.
Chest and Bone Pain
Chest and bone pain can make it difficult to exercise, but it’s crucial to stay active to manage diabetes. Low-impact exercises like walking or using an elliptical machine can help reduce pain while improving cardiovascular health. A personal trainer can also help you develop an exercise plan that strengthens your bones and improves posture.
Overweight and Obesity
Being overweight or obese can make it difficult to manage diabetes, but regular exercise can help you lose weight and improve blood sugar control. A personal trainer can help you develop an exercise plan that is safe and effective for your individual needs.
As you can see, there are many challenges to managing diabetes as a senior, but regular exercise can help you overcome them. With the help of a certified personal trainer, you can develop an exercise plan that is safe, effective, and tailored to your individual needs.
“Exercise is medicine, and it’s the most underutilized medicine in the world.” – Dr. Jordan Metzl
Conclusion
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can have a significant impact on your diabetes management. This is especially true for seniors who may be at a higher risk for developing diabetes-related complications. By engaging in physical activity, you can improve your blood glucose control, reduce cardiovascular risk factors, and contribute to weight loss.
It’s important to remember that exercise doesn’t have to be intense to be effective. Even light physical activity, such as walking or gardening, can provide health benefits. You should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week.
When exercising, it’s important to monitor your blood glucose levels regularly. This will help you avoid hypoglycemia and ensure that your blood glucose levels stay within a healthy range. You may also need to adjust your medication or insulin dosage to account for changes in physical activity.
For men and women with diabetes, it’s important to choose activities that you enjoy and that fit into your lifestyle. This will help you stick to your exercise routine and make it a sustainable habit. You may also want to consider exercising with a friend or joining a group fitness class to stay motivated and accountable.
As you age, it’s normal for your body to experience changes that can make exercise more challenging. However, this doesn’t mean that you should stop being physically active. In fact, regular exercise can help you maintain your strength, flexibility, and balance as you age.
In the words of Dr. Ronald Sigal, a professor of medicine at the University of Calgary, “Exercise is medicine, and it’s one of the most powerful medicines that we have.” By incorporating exercise into your routine, you can take control of your diabetes management and improve your overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some low-impact exercises that are suitable for seniors with diabetes?
Seniors with diabetes can benefit from low-impact exercises, which are gentle on the joints and help improve cardiovascular health. Some low-impact exercises that are suitable for seniors with diabetes include walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga. These activities can be done at a moderate pace and can be adjusted to suit the individual’s fitness level.
How can seniors with diabetes safely exercise at home?
Seniors with diabetes can safely exercise at home by following some simple guidelines. They should start with a warm-up to get their muscles ready for exercise and avoid sudden movements that could cause injury. They should also wear comfortable and supportive
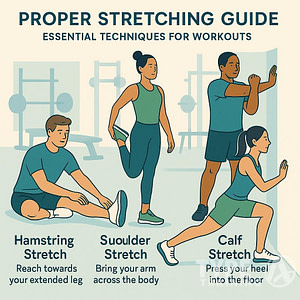
What are some stretching exercises that can benefit seniors with diabetes?
Stretching exercises can help seniors with diabetes improve their flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and prevent injuries. Some stretching exercises that can benefit seniors with diabetes include shoulder rolls, neck stretches, hamstring stretches, and calf stretches. Seniors should hold each stretch for 10-30 seconds and repeat each stretch 2-4 times.
What are some morning exercises that are safe for seniors with diabetes?
Morning exercises can help seniors with diabetes start their day off on the right foot and improve their energy levels. Some morning exercises that are safe for seniors with diabetes include walking, yoga, tai chi, and chair exercises. These exercises can be done indoors or outdoors and can be adjusted to suit the individual’s fitness level.
What precautions should seniors with diabetes take when exercising?
Seniors with diabetes should take some precautions when exercising to avoid injury and maintain their health. They should check their blood glucose levels before and after exercising and have a snack or glucose tablets on hand in case of low blood sugar. Seniors should also start with a warm-up and cool-down and avoid sudden movements that could cause injury. They should also wear comfortable and supportive
What are some recommended exercises for seniors with diabetes and high blood pressure ?
Seniors with diabetes and high