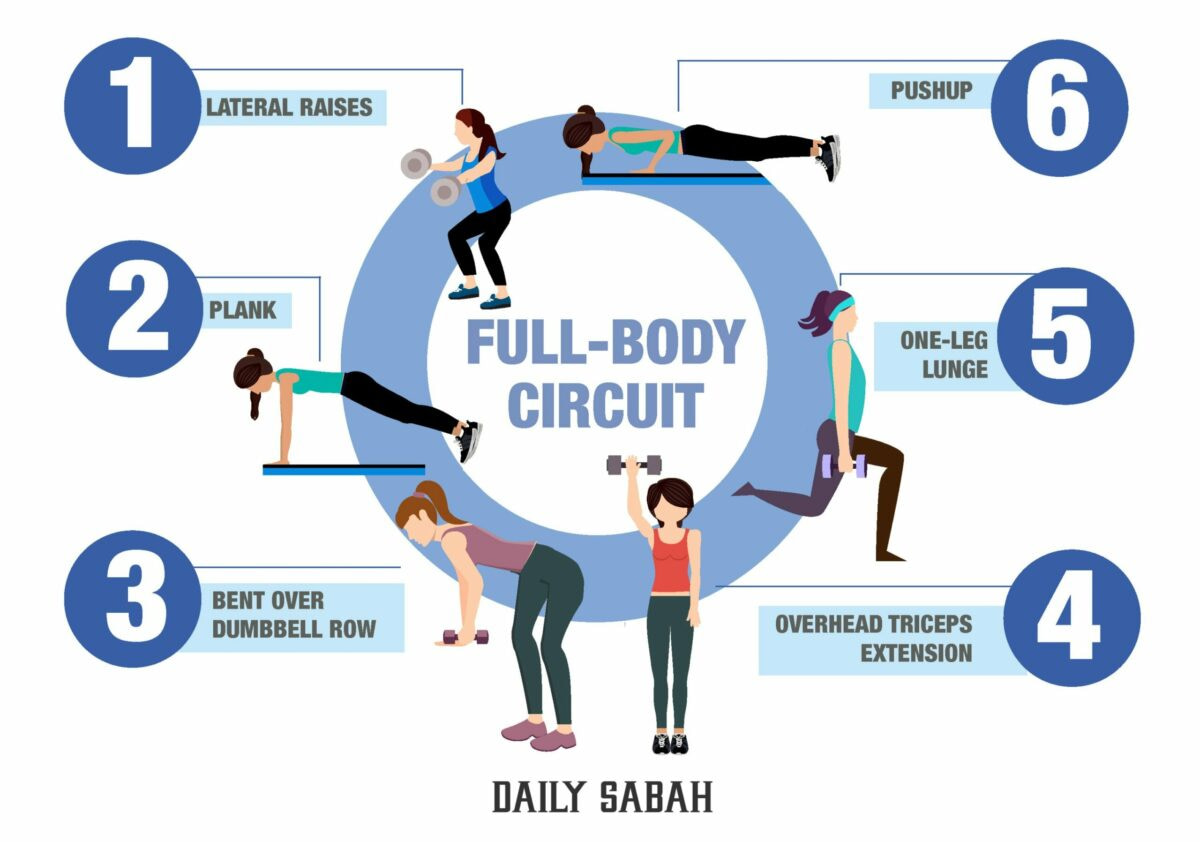
Circuit training is an efficient form of exercise designed to stimulate different muscle groups through a sequence of workouts with minimal rest in between. This approach to fitness not only helps you build strength but also enhances your cardiovascular health due to the fast-paced nature of the workout. Each circuit can consist of up to 10 different exercises, allowing you to target various aspects of physical fitness within a single session.
By rotating through a series of exercises, you work out multiple muscle groups, getting a full-body workout that can improve muscle tone and functional strength. Because circuit training involves little to no rest between the exercises, it also gives you the added benefit of an aerobic workout, contributing to improved heart health and fat burn.
With its structure and intensity, circuit training can be tailored to your individual fitness goals, whether you’re looking to lose weight, build muscle, or improve endurance. This adaptability makes it a suitable option for a wide range of fitness enthusiasts, from beginners to advanced athletes.
Understanding Circuit Training
Popular posts:
Circuit training is an efficient blending of strength training and cardiovascular exercise designed to improve your fitness levels and strengthen various muscle groups in a single workout session.
Defining Circuit Training
Circuit training is a form of resistance training that involves a series of exercises, or “stations,” completed one after another with minimal rest in between. Each station targets different muscle groups to ensure a full-body workout. The exercises typically involve a mix of weights, bodyweight movements, and cardio exercises. The high-intensity nature of circuit training can help you increase muscular strength and endurance as well as cardiovascular fitness.
Comparing Circuit to Traditional Workouts
Unlike traditional workouts, which often separate strength training from cardiovascular exercises, circuit training seamlessly integrates both. Traditional workouts may focus on one muscle group per session, whereas circuit training involves multiple muscle groups and exercise types in a single session. This approach is known to maximize calorie burn and efficiency, making it a time-effective workout choice for those looking to achieve comprehensive fitness results.
Essential Components of Circuit Workouts
To maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of your circuit workouts, it’s imperative to prioritize exercise selection, circuit structuring, and rest period management.
Exercise Selection
Choosing the right exercises is crucial for a balanced circuit. Aim to include a mix of strength training, cardiovascular movements, and flexibility exercises. For strength, consider squats or deadlifts, and integrate cardio exercises like jumping jacks or high knees to boost heart rate. Flexibility moves such as stretching or yoga poses can enhance recovery. A variety of exercises ensures you’re challenging different muscle groups.
Structuring Circuits
Circuits should be arranged to alternate between muscle groups, allowing one group to recover while another is at work. A typical structure might cycle through lower body, upper body, core, and cardio exercises. For instance, follow a lunging exercise with a set of push-ups before moving on to abdominal crunches. This rotation not only prevents muscle fatigue but also keeps your workout dynamic.
Determining Rest Periods
Rest periods between exercises should be short to maintain intensity but long enough for brief recovery. Generally, rest for about 15-30 seconds after each exercise. During circuit workouts, you’ll typically perform each exercise for a set duration, like 30 seconds to a minute, or for a specific number of reps. Your overall workout routine could last anywhere from 20 to 60 minutes. Tailor the time and rest based on your fitness level and goals, considering advice from Nerd Fitness or Verywell Health to implement an effective routine.
Benefits of Circuit Training
Circuit training offers a range of advantages that can significantly improve your fitness regimen. It combines cardiovascular exercise with strength training, allowing you to reap the multifaceted benefits of an integrated workout.
Improving Cardiovascular Health
Circuit training is an efficient way to enhance your cardiovascular health. By transitioning quickly between exercises with little rest, your heart rate remains elevated throughout the workout. This constant movement helps to strengthen your heart, improving overall heart health and endurance.
Enhancing Muscular Strength
Building muscular strength is a key benefit of circuit training. The workout targets various muscle groups by incorporating resistance exercises, such as weight lifting, push-ups, or bodyweight squats. This variety not only prevents muscle imbalances but also promotes comprehensive muscular development.
Maximizing Calorie Burn
If weight loss is your goal, circuit training can be highly effective. This high-intensity workout maximizes calorie burn during and after your workout, due to the phenomenon of excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). Your body continues to burn calories at an increased rate as it recovers, which can contribute to weight management and fat loss.
Tailoring Workouts to Fitness Goals
To achieve your specific fitness objectives, it’s crucial to design your workouts with your goals in mind. Whether you’re aiming to shed fat, enhance strength and endurance, or gain muscle, each target requires a unique approach to your workout regimen.
Fat Loss Focus
For fat loss, a circuit training workout should be structured to create a high-intensity session that keeps your heart rate elevated. You can perform exercises back-to-back with minimal rest in between, such as 30-60 seconds of burpees followed by a similar duration for other aerobic workouts, which may include jumping jacks, mountain climbers, or high-knees. Include strength training exercises with higher repetitions and moderate weight to sustain muscle mass as you reduce body fat.
Building Strength and Endurance
To build strength and endurance, focus on a blend of compound movements at a challenging weight that allows for 8-15 reps. These movements might consist of deadlifts, squats, or bench presses, integrated with short bursts of cardiovascular activity. For instance, after a set of squats, include a quick 1-minute cardio interval. Adequate rest in between sets is also essential to allow for muscle recovery and to maintain the quality of your strength training.
Designing for Muscle Gain
When muscle gain is the aim, prioritize exercises that target multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Segments of your circuit might include lower reps at heavier loads focused on exercises like the bench press or pull-ups, followed by isolated movements such as bicep curls or tricep extensions to fatigue individual muscles. Rest periods should be longer to promote maximum muscle recovery and growth.
Creating an Effective Circuit Training Plan
To set yourself up for success in circuit training, you need to start at a level that matches your current fitness abilities and plan a progression that keeps you challenged as you get stronger and more adept.
Planning for Beginners
If you’re new to circuit training, it’s essential to focus on establishing a solid foundation. Begin with exercises that you can perform with proper form to minimize the risk of injury. Your initial workout routine should involve a full-body workout to ensure balanced muscle development. An effective beginner circuit might include:
- Bodyweight squats
- Assisted push-ups
- Bent-over rows with light weights
- Step-ups on a box
- Plank holds
Perform each exercise for 10 to 15 repetitions, ensuring you manage each with good form. Allow for at least 30 seconds of rest between exercises. Repeat the circuit 2-3 times, with a minute of rest between circuits. Work out with this plan 2-3 times per week.
Advancing to Intermediate Levels
As your fitness level increases, you can customize your circuit to become more challenging. To transition into an intermediate level, incorporate variations of basic exercises and increase intensity:
- Squats with a dumbbell press
- Push-ups with elevated feet
- Bent-over rows with heavier weights or kettlebells
- Box jumps
- A 45-second plank or side planks
At the intermediate phase, aim for 15-20 repetitions per exercise or set a timer for 30-45 seconds of continuous work with 15-30 seconds of rest. Perform 3-4 rounds of the circuit and try to include a mix of resistance training, cardio, and core exercises. You should now be comfortable with these workouts 3-4 times a week.
Remember, progress at your own pace, listen to your body, and adjust the exercise load and intensity according to your own fitness improvements.
Exercise Examples and Variations
In circuit training, workout variations are crucial for engaging different muscle groups and preventing monotony. Below you’ll find targeted exercises to include in your routine, focusing on upper body, lower body, and core stability.
Upper-Body Exercises
For the upper body, incorporating a variety of exercises ensures a balanced workout. Start with push-ups to target your chest, shoulders, and triceps. You can modify the intensity by changing hand placements or elevating your feet. Another effective exercise is the bicep curl, which can be performed with dumbbells, resistance bands, or even household items for muscle growth and endurance.
- Push-Ups:
- Standard push-ups: Keep your body in a straight line from head to heels.
- Elevated push-ups: Place your feet on a raised surface to increase intensity.
- Bicep Curls:
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, dumbbells in hand, palms facing forward, and curl weights towards your shoulders.
Lower-Body Exercises
Your lower body foundation is built on exercises like squats and lunges. Squats work on your quads, hamstrings, and glutes, while lunges focus on similar muscle groups with an emphasis on balance and coordination. Keep your form strict to maximise benefits and minimize injury risk.
- Squats:
- Stand with feet a bit wider than shoulder-width apart and lower your body as if sitting back in a chair.
- Lunges:
- Step forward with one foot and lower your hips until both knees are bent at a 90-degree angle.
Core and Stability Exercises
For core strength, engage in exercises like planks which target the entire abdominal region as well as the lower back and shoulders. Mountain climbers combine core engagement with cardiovascular benefits, making them a dual-purpose exercise.
- Plank:
- Enter push-up position and hold, keeping your body straight and abs engaged.
- Mountain Climbers:
- From the plank position, alternate driving your knees towards your chest at a quick pace.
By combining these exercises into a circuit, you can create a balanced, full-body workout that challenges various muscle groups and keeps your exercises fresh and effective.
Incorporating Equipment and Bodyweight
In circuit training, the harmony between using equipment and implementing bodyweight exercises creates a comprehensive workout. You have the flexibility to customize your routine to suit your goals, whether you’re at the gym or at home.
Utilizing Free Weights
Free weights, like dumbbells and kettlebells, are versatile tools for strength-building within circuit training. Consider the following approach:
- Upper Body: Incorporate exercises such as bicep curls and shoulder presses to target the arms and shoulders.
- Lower Body: Goblet squats and kettlebell swings can effectively work your leg and glute muscles.
- Core Engagement: Dumbbell Russian twists and weighted planks intensify your core workout.
Remember, the weight you choose should be challenging but manageable to maintain good form throughout the circuit.
Leveraging Bodyweight Movements
Your body is your equipment. Effective bodyweight exercises can enhance strength, flexibility, and balance:
- Upper Body: Push-ups and pull-ups challenge multiple muscle groups, enhancing overall upper body strength.
- Lower Body & Core: Exercises like bodyweight squats, lunges, and planks engage your core while also toning your legs.
- Agility & Cardio: Incorporate jumps, burpees, and mountain climbers to increase heart rate and improve cardiovascular fitness.
By alternating between bodyweight movements and free weight exercises, you can create a balanced workout that promotes muscle endurance and cardiovascular health.
Safety and Injury Prevention
When embarking on circuit training workouts, your safety is paramount. Being mindful of how you execute each exercise and how you organize your training progression can dramatically decrease the risk of injury.
Understanding Proper Form
Proper form is crucial for every exercise in a circuit. This involves aligning your body correctly and moving smoothly through the range of motion. Neglecting form can lead to strains or sprains. For instance, when performing squats, your feet should be shoulder-width apart, and you should push your hips back while keeping your back straight. Here’s a guide to get you started with the basics of circuit training exercises.
- Key Points:
- Alignment: Ensure joints are correctly aligned; knees should not bow inward or outward during lower body exercises.
- Movement: Move through exercises with control—avoid jerky, uncontrolled motions that can cause injury.
Devising a Safe Progression Strategy
Your progression strategy should be gradual and personalized. Start with lighter weights or easier variations of exercises and increase the intensity incrementally. A safe progression helps you build strength and endurance without overloading your muscles. Before adding more weight or complexity, be sure you can maintain proper form.
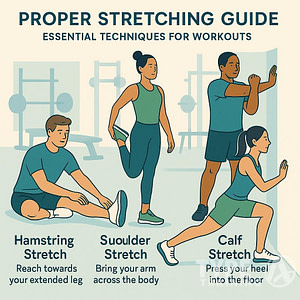
- Warm-up: Begin each session with a warm-up to prepare your muscles and joints. Dynamic stretches and light aerobic activity can increase blood flow and reduce your risk of injury.
- Stretch: After your workouts, take time to cool down and focus on stretching the major muscle groups you’ve worked to aid in recovery and prevent stiffness.
By honing your form and responsibly progressing your routine, you safeguard your well-being while pursuing fitness through circuit training.
Measuring Progress and Making Adjustments
In circuit training, tracking your improvement and knowing when to modify your routine are crucial for continuous development. These strategies ensure that you’re not only meeting your fitness goals but also pushing past any plateaus to reach new heights in your physical potential.
Tracking Workouts
It’s essential to document each workout session. Use a log or a digital timer to track the time spent on each exercise. Take note of the number of repetitions, the weight you lifted, and the rest intervals between circuits. Over time, this data will reveal your progress and inform you about when to increase the intensity or volume of your workouts. Keeping a detailed record can highlight patterns and provide insights for improvement, as supported by Verywell Fit.
Adjusting for Plateaus and Progress
When you detect a plateau, or notice significant progress, it’s time to modify your workout plan. If the current workout is no longer challenging, increase the weight, change the exercises, or reduce rest periods. For plateaus, discuss alternative strategies with a personal trainer who can provide personalized advice based on your fitness level. On the other hand, when you surpass your goals, consider new ones to maintain motivation and progression.
Related: 20 Tips for Overcoming Fitness Plateaus and Staying Motivated
Integrating Circuit Training into a Busy Lifestyle
Circuit training offers the flexibility to fit high-intensity workouts into your hectic schedule, providing a variety of exercises that can be done anywhere, saving you time without sacrificing fun or efficiency.
Short and Effective Workouts
Busy lifestyles demand efficient time management and circuit training is tailored for just that. You can experience a robust workout in as little as 15 to 30 minutes by focusing on high-intensity circuit training. These workouts combine both strength training and aerobic elements, allowing you to improve muscle strength and cardiovascular health simultaneously. Here’s a quick guide:
- Plan Ahead: Outline your workout with 8-10 exercises.
- Use Time Wisely: Perform each exercise for a set period, such as 45 seconds, with minimal rest.
- Cycle Through: Complete the circuit 2-3 times for a full workout.
Circuit Training While Traveling
Traveling doesn’t mean your workouts must pause. Circuit training is versatile and can adapt to cramped hotel rooms or a park.
- Pack Smartly: Bring resistance bands or a jump rope; they’re lightweight and portable.
- Improvise: Use bodyweight exercises like push-ups, squats, and lunges.
- Stay Consistent: Schedule your workouts as you would any other meeting during your travel.
By incorporating these methods, you maintain your workout regimen and adapt fitness to your busy life, regardless of location.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, you’ll find specific information on the key aspects of circuit training. From weight loss benefits to incorporating weights into your routines, these FAQs will guide you through understanding and getting started with circuit training.
What are the primary benefits of engaging in circuit training?
Circuit training is recognized for its efficiency in improving cardiovascular endurance, increasing muscle strength, and promoting weight loss. It allows you to maximize your workout time by blending strength and aerobic exercises, delivering a comprehensive fitness experience.
How can circuit training be used effectively for weight loss?
By combining high-intensity exercises with minimal rest between stations, circuit training keeps your heart rate elevated, which can increase calorie burn and fat loss. Consistent circuit workouts, when paired with a balanced diet, can be a powerful strategy for weight loss.
What types of exercises are commonly included in a full-body circuit workout?
A full-body circuit workout typically includes a variety of exercises targeting all major muscle groups, such as squats, lunges, push-ups, planks, and burpees. This range of exercises ensures balanced muscle development and prevents overuse injuries.
How can beginners get started with circuit training workouts?
Beginners should start with simple, low-intensity exercises to establish good form. They can begin with bodyweight activities, such as modified push-ups or assisted lunges, before gradually incorporating weights and increasing intensity as they develop strength and confidence.
What is the recommended structure for a circuit training session to enhance muscular endurance?
To enhance muscular endurance, you can structure your circuit to include lighter weights with higher repetitions and shorter rest intervals. This approach promotes sustained effort, which can lead to improved muscle stamina over time.
Can circuit training with weights be incorporated into a home workout routine, and if so, how?
Certainly, you can incorporate weights into your home circuit workouts by using dumbbells, resistance bands, or even household items. Performing exercises like dumbbell presses or kettlebell swings can add resistance, making the workout more challenging and effective.